Abstract
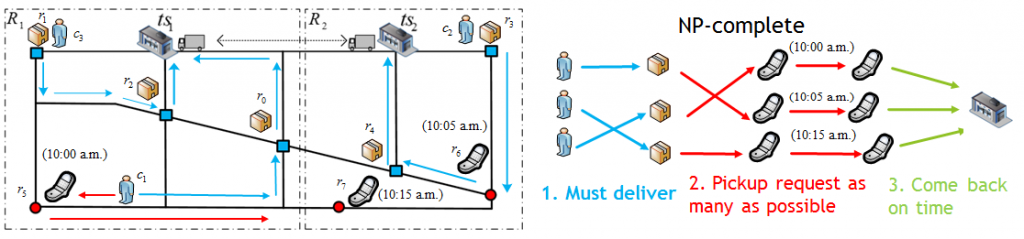
City express services are in great demand in recent years. However, the current city express system is found to be unsatisfactory for both the service providers and customers. In this paper, we are the first to systematically study the large-scale dynamic city express problem. We aim to increase both the effectiveness and the efficiency of the scheduling algorithm. To improve the effectiveness, we adopt a batch assignment strategy that computes the pickup-delivery routes for a group of requests received in a short period rather than dealing with each request individually. To improve the efficiency, we design a two-level priority queue structure to reduce redundant shortest distance calculation and repeated candidate generation. We develop a simulation system and conduct extensive performance studies in the real road network of Beijing city. The experimental results demonstrate the high effectiveness and efficiency of our algorithm.